Is your gearbox running hotter than usual? Overheating isn’t just a minor inconvenience—it’s a warning sign of deeper issues that can lead to costly repairs, reduced efficiency, and even environmental harm. From mechanical misalignments and lubrication failures to blocked cooling systems, multiple factors can push your gearbox into the danger zone. Left unchecked, excessive heat accelerates wear on critical components like gears and bearings, slashes fuel efficiency, and risks toxic emissions.
But the good news? Most overheating problems are preventable. In this guide, we’ll break down the root causes, actionable fixes, and proactive maintenance tips to keep your gearbox cool, efficient, and reliable. Whether you’re troubleshooting minor heat spikes or overhauling your system, these insights will help you safeguard performance and avoid downtime. Let’s dive in!

Common Causes of Gearbox Overheating
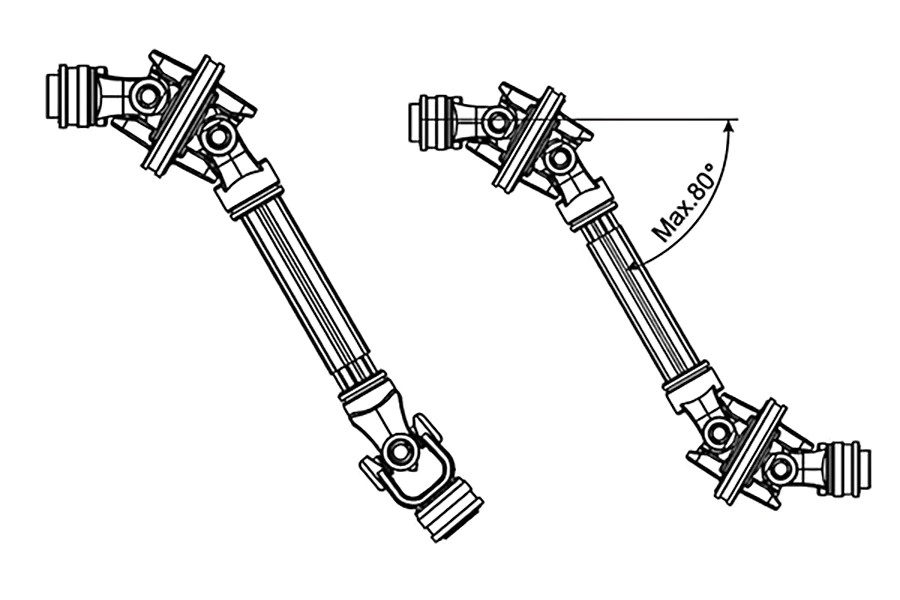
- Excessive Internal Heat Generation: The first scenario is bearing issues. Tight installation, damaged cages, or misaligned inner/outer races increase friction and heat. The second scenario is gear misalignment: Incorrect gear meshing (e.g., improper side clearance) raises friction and heat production.
- Cooling System Failures: Blocked heat dissipation channels or poor cooling system design prevent heat from escaping, leading to rapid temperature spikes.
- Lubrication Problems: When the gearbox is over-lubrication, excess oil creates thick films between components, increasing friction resistance and heat. When the gearbox is under-lubrication, insufficient or low-viscosity oil fails to reduce metal-to-metal contact, generating excessive heat. When using degraded oil to lubricate the gearbox, ontaminated or oxidized oil loses cooling efficiency, worsening heat retention.
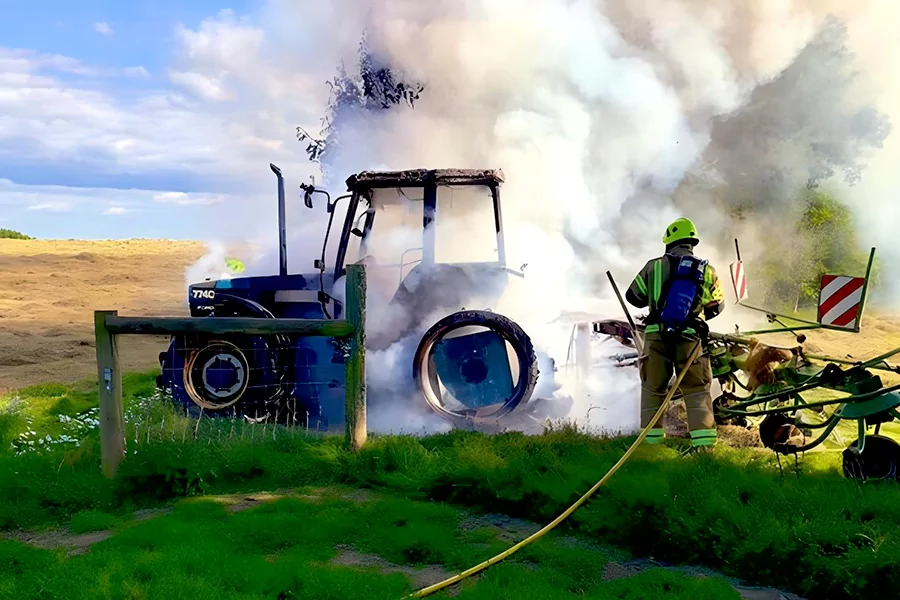
Consequences of Overheating
- Component Wear: High temperatures accelerate wear on gears and bearings, shortening service life.
- Performance Loss: Increased friction reduces power transmission efficiency and raises fuel consumption.
- Environmental Impact: Oil leakage or combustion leads to toxic emissions, damaging catalytic converters.
Effective Solutions
- Lubrication Maintenance: To maintain optimal lubrication performance, always replace degraded oil and filters as soon as signs of wear appear, adhering strictly to the manufacturer’s guidelines for oil type and quantity. Additionally, ensure oil circulation systems—including pumps and pipes—are kept clean and fully functional to prevent blockages and guarantee smooth oil flow throughout the gearbox.
- Cooling System Optimization: To further improve heat dissipation efficiency, install auxiliary coolers (air or water-based) to reduce internal temperatures. Similarly, clean clogged radiator grids thoroughly to eliminate airflow restrictions and ensure consistent cooling performance across the gearbox.
Mechanical Adjustments: To reduce friction and heat generation, prioritize correcting gear alignment and adjusting meshing clearances for smooth operation. Additionally, inspect bearings regularly and replace damaged ones promptly to eliminate excessive heat sources and ensure long-term gearbox efficiency.
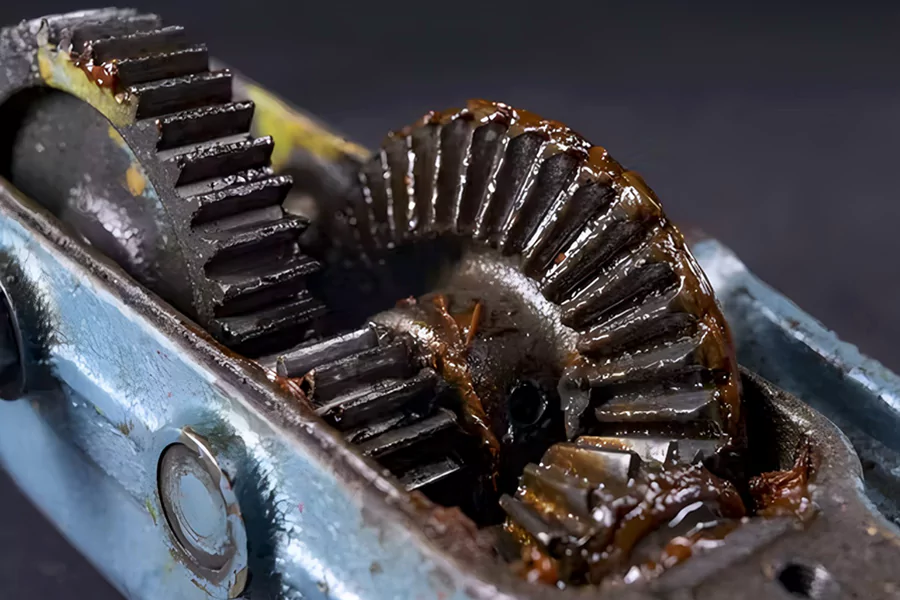

Preventive Measures
- Regular Inspections: Monitor oil quality, component wear, and cooling efficiency during routine maintenance.
- Operational Habits: Avoid prolonged low-speed driving or frequent gear shifts to prevent clutch slippage and overheating.
- Upgrade Components: Consider high-performance bearings or heat-resistant materials for heavy-duty applications.
Key Takeaways
Gearbox overheating stems from friction, lubrication issues, and cooling failures. Regular maintenance, proper lubrication, and system upgrades are critical for prevention. Addressing minor issues early avoids costly repairs and downtime. If DIY fixes fail, consult certified technicians for advanced diagnostics, such as thermal imaging or vibration analysis.